
الگوریتم مرتب سازی سریع (Quick Sort)
الگوریتم مرتب سازی سریع (Quick Sort) مانند الگوریتم Merge Sort، به روش تقسیم و غلبه (Divide and Conquer) عمل می کند. در این الگوریتم یک عنصر به عنوان محور انتخاب می شود و آرایه با توجه به آن عنصر تقسیم می شود. روش انتخاب عنصر محوری در نسخه های مختلف الگوریتم مرتب سازی سریع متفاوت است.
- همیشه عنصر اول به عنوان عنصر محوری انتخاب می شود.
- همیشه عنصر آخر به عنوان عنصر محوری انتخاب می شود (در زیر پیاده سازی شده است).
- یک عنصر تصادفی به عنوان عنصر محوری انتخاب می شود.
- عنصر میانی به عنوان عنصر محوری انتخاب می شود.
عملیات اصلی در الگوریتم مرتب سازی سریع، پارتیشن بندی است. هدف از پارتیشن بندی این است که در آرایه داده شده، یک عنصر به عنوان عنصر محوری انتخاب و در موقعیت مناسب قرار داده شود. سپس عناصری که از این عنصر کوچکتراند، به قبل از آن و عناصری که بزرگتراند، به بعد از آن انتقال یابند.
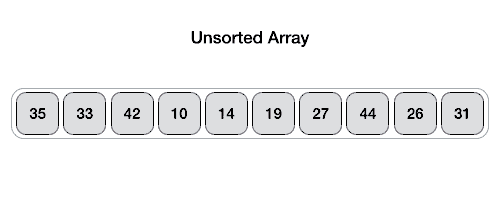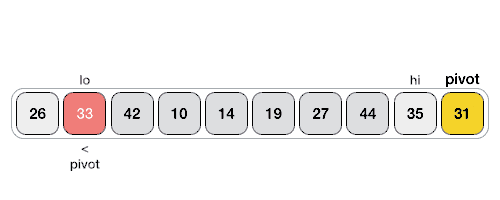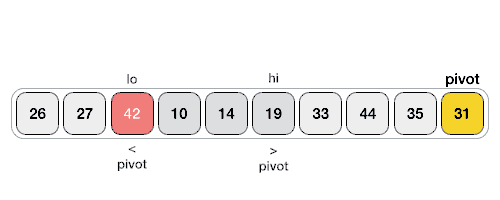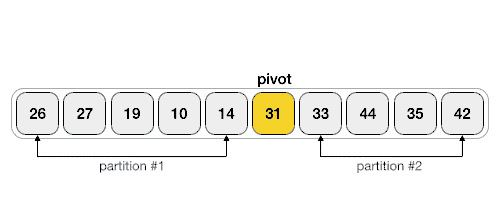
شبه کد مربوط به تابع Quick Sort به صورت بازگشتی:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | /* low --> Starting index, high --> Ending index */ quickSort(arr[], low, high) { if (low < high) { /* pi is partitioning index, arr[pi] is now at right place */ pi = partition(arr, low, high); quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1); // Before pi quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high); // After pi } } |
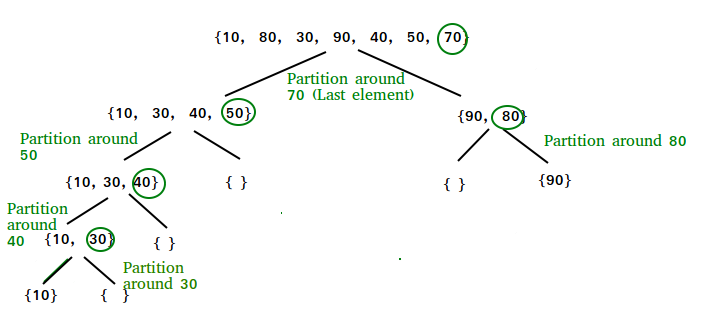
الگوریتم پارتشین بندی:
راه های زیادی برای انجام پارتیشن بندی آرایه وجود دارد. منطق کار ساده است، از سمت چپ ترین عنصر شروع می کنیم و به دنبال عناصری که کوچکتر از i (یا برابر با آن) هستند، می گردیم. اگر عنصر کوچکتری پیدا کردیم، آن را با arr[i] جا به جا می کنیم. در غیر این صورت این عنصر را نادیده می گیرم.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | /* low --> Starting index, high --> Ending index */ quickSort(arr[], low, high) { if (low < high) { /* pi is partitioning index, arr[pi] is now at right place */ pi = partition(arr, low, high); quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1); // Before pi quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high); // After pi } } |
شبه کد مربوط به تابع partition:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | /* This function takes last element as pivot, places the pivot element at its correct position in sorted array, and places all smaller (smaller than pivot) to left of pivot and all greater elements to right of pivot */ partition (arr[], low, high) { // pivot (Element to be placed at right position) pivot = arr[high]; i = (low - 1) // Index of smaller element for (j = low; j <= high- 1; j++) { // If current element is smaller than the pivot if (arr[j] < pivot) { i++; // increment index of smaller element swap arr[i] and arr[j] } } swap arr[i + 1] and arr[high]) return (i + 1) } |
مراحل پارتشین بندی:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | arr[] = {10, 80, 30, 90, 40, 50, 70} Indexes: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 low = 0, high = 6, pivot = arr[h] = 70 Initialize index of smaller element, i = -1 Traverse elements from j = low to high-1 j = 0 : Since arr[j] <= pivot, do i++ and swap(arr[i], arr[j]) i = 0 arr[] = {10, 80, 30, 90, 40, 50, 70} // No change as i and j // are same j = 1 : Since arr[j] > pivot, do nothing // No change in i and arr[] j = 2 : Since arr[j] <= pivot, do i++ and swap(arr[i], arr[j]) i = 1 arr[] = {10, 30, 80, 90, 40, 50, 70} // We swap 80 and 30 j = 3 : Since arr[j] > pivot, do nothing // No change in i and arr[] j = 4 : Since arr[j] <= pivot, do i++ and swap(arr[i], arr[j]) i = 2 arr[] = {10, 30, 40, 90, 80, 50, 70} // 80 and 40 Swapped j = 5 : Since arr[j] <= pivot, do i++ and swap arr[i] with arr[j] i = 3 arr[] = {10, 30, 40, 50, 80, 90, 70} // 90 and 50 Swapped We come out of loop because j is now equal to high-1. Finally we place pivot at correct position by swapping arr[i+1] and arr[high] (or pivot) arr[] = {10, 30, 40, 50, 70, 90, 80} // 80 and 70 Swapped Now 70 is at its correct place. All elements smaller than 70 are before it and all elements greater than 70 are after it. |
پیاده سازی الگوریتم Quick Sort
در زیر می توانید پیاده سازی الگوریتم مرتب سازی سریع در زبان سی پلاس پلاس را مشاهده کنید:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 | /* C++ implementation of QuickSort */ #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // A utility function to swap two elements void swap(int* a, int* b) { int t = *a; *a = *b; *b = t; } /* This function takes last element as pivot, places the pivot element at its correct position in sorted array, and places all smaller (smaller than pivot) to left of pivot and all greater elements to right of pivot */ int partition (int arr[], int low, int high) { int pivot = arr[high]; // pivot int i = (low - 1); // Index of smaller element for (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++) { // If current element is smaller than the pivot if (arr[j] < pivot) { i++; // increment index of smaller element swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]); } } swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]); return (i + 1); } /* The main function that implements QuickSort arr[] --> Array to be sorted, low --> Starting index, high --> Ending index */ void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) { if (low < high) { /* pi is partitioning index, arr[p] is now at right place */ int pi = partition(arr, low, high); // Separately sort elements before // partition and after partition quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1); quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high); } } /* Function to print an array */ void printArray(int arr[], int size) { int i; for (i = 0; i < size; i++) cout << arr[i] << " "; cout << endl; } // Driver Code int main() { int arr[] = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5}; int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1); cout << "Sorted array: n"; printArray(arr, n); return 0; } |
خروجی:
1 2 | Sorted array: 1 5 7 8 9 10 |
تغییر به حالت نزولی
برای تغییر به حالت نزولی کافیست در تابع partition شرط if (arr[j] < pivot) را به if (arr[j] > pivot) تغییر دهید.
بررسی الگوریتم Quick Sort
در حالت کلی زمان سپری شده توسط این الگوریتم را می توانیم به شکل زیر بنویسیم:
1 | T(n) = T(k) + T(n-k-1) + (n) |
دو بخش اول مربوط به فراخوانی های بازگشتی و بخش سوم هم مربوط به عملیات پارتیشن بندی است. K تعداد عناصر کوچکتر از عنصر محوری (pivot) است. میزان زمان سپری شده توسط الگوریتم Quick Sort به آرایه ورودی و استراتژی پارتیشن بندی بستگی دارد.
- پیچدگی زمانی در بدترین حالت برابر است با O(n2).
- پیچدگی زمانی در بهترین حالت O(nlog n) برای پارتیشن بندی ساده و O(n) برای پارتیشن بندی سه جانبه و کلیدهای برابر.
- پیچدگی زمانی در حالت متوسط برابر است با O(nlog n).









 (44 امتیاز از 9 رای)
(44 امتیاز از 9 رای)



















هیچ نظری ثبت نشده است